

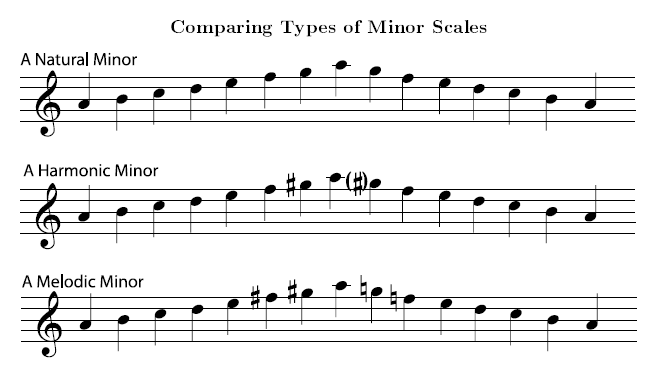
Major and minor keys share two different relationships.These are largely the same in minor as they are in major, except for the subtonic (te or \downarrow\hat7). Each note of a minor scale is also named with scale-degree names.There are a few new solfège syllables in minor including me (\downarrow\hat3), le (\downarrow\hat6)), and te (\downarrow\hat7)). Scale degrees in minor are the same as those in major.The melodic minor form of the minor scale consists of an ordered collection of half- and whole-steps in the ascending succession W-H-W-W-W-W-H and the descending succession W-W-H-W-W-H-W.The harmonic minor form of the minor scale consists of an ordered collection of half- and whole-steps in the ascending succession W-H-W-W-H-3Hs-H.The natural minor form of the minor scale consists of an ordered collection of half- and whole-steps with the ascending succession W-H-W-W-H-W-W.A minor scale's third note is always a half-step lower than the third note of the major scale with the same name.Two-octave minor scales can be found here:Īrpeggios (or arpeggi, which is the correct plural of the Italian term arpeggio) are like scales, but only made up of the first, third and fifth notes of a scale. To play the melodic minor scale, play both parenthesized alterations when going up, and ignore both when going down.To play the harmonic minor scale, ignore only the first parenthesized alteration.To play the natural minor scale, ignore the parenthesized alterations.To complicate things even further, the melodic variant is usually played only when going up the scale ( ascending scale),īut is replaced by the natural scale when going down ( descending scale).īelow you can find all the minor scales, with all the possible alterations. The melodic minor scale, in which both the sixth and the seventh degrees are raised by a half step.The harmonic minor scale, in which the seventh degree is raised by a half step.The natural minor scale, which is the one we have discussed so far.Now, to be more precise there are actually three different kinds of minor scale. The simplest minor scale to write or play is A minor, since it's the only minor scale that requires no sharps or flats You play the major scale that begins on the same note, but flatting the third, sixth, and seventh notes. There's also another method to figure out the key signature: The key signature of any minor scale by using this procedure. So if you know the key signatures of all the major scales you can derive This means that the key signature for D minor is the same used to play F major. So the relative major of D minor is F major. Signature of D minor, count 3 half steps up from D: Eb, E, F. To figure out a minor scale's relative major, justĬount up three half steps from the name of the minor scale. You start on the note the scale is named for just like for a major scale, but you use the This means that when playing a minor scale That's because every minor scale has a relative major. You may observe that there's a relation between the schemes on which major and minor scales are built. So there's a total of five whole steps (you can count them).īy the way, these notes that fall in between the notes of a scale without belonging to it are called chromatic notes. On the other hand, if you take C and D, there's C# in between: they are separated by a “whole step”.
You'll immediately notice that there are no notes between B and C: that's what we meant by “half step”. The highlighted notes form the A minor scale. Just be content to know that all western music is based on this twelve-note system). (explaining what this is and where it comes from is far beyond our scopes. Here you can see all the notes in the modern twelve-tone equal temperament The sequence is the same for all minor scales: one whole step, one half step, two whole steps, one half step, two whole steps (W, H, W, W, H, W, W).įor example, consider the A minor scale: A The minor scale is one of the diatonic scales, meaning that it is made up of five whole steps and two half steps. (or a natural when the 7th degree has a flat in the key signature). Please note that the 7th degree cannot be called “leading tone” unless it is raised by a semitone with a sharp These notes are assigned different names:
DESCENDING NATURAL AND MELODIC MINOR SCALES PLUS
Is made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth which duplicates the first one an octave higher. In music theory, a minor scale (also known as aeolian scale)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
